How Much Conflict Is Acceptable in a Family
Understanding Conflict in the Family Business concern
Professor John A. Davis
Founder and Chairman, Cambridge Family unit Enterprise Group; Senior Lecturer and Faculty Director, Family unit Enterprise Programs, MIT Sloan School of Management
Courtney Collette
Partner and Senior Advisor, Cambridge Advisors to Family Enterprise; COO, Cambridge Institute for Family unit Enterprise


Peradventure some time, walking in a garden or arboretum, y'all've happened across a pleached tree. Pleaching is the process of planting 2 or more immature, flexible copse close to one another and weaving their trunks together equally they abound. The process requires time and attention to guide the trunks and aid them intertwine, but pleaching creates a very potent combined plant. Strong families are similar a well-pleached tree. On the other mitt, like fractured families, if the conjoined trunks are untended, they will naturally diverge and tin harden in the wrong direction, non only ruining the visual effect, only weakening the combined tree.

Achieving a well-pleached business family is challenging for a number of reasons. It goes without maxim that there are many opportunities for business family members to have conflicts, given all the ways in which their lives intersect and their interests or ideas may be out of synch.
One of the goals of a business family is to learn how to manage disharmonize inside the family then that good family unit decisions surface, individuals grow in healthy ways, and relationships reach their potential.
Every bit much as nosotros prefer peace and harmony in our family, nosotros usually tolerate pocket-size skirmishes and can even see the value of conflicts that generate better thinking and solutions on a subject. What we fear, and commonly do a poor task of managing however, is disharmonize that divides people, harms their relationships, and makes agreements and solutions to problems fifty-fifty harder to put in place.
In this article, nosotros volition assistance you ameliorate empathise the origin and nature of different kinds of conflict in business families. This can be a starting betoken to assistance you amend manage family unit conflict in your business family so that you can help family relationships and the family business concern to grow strong and salubrious, like a well-pleached tree.
Four Kinds of Business concern Family Conflict
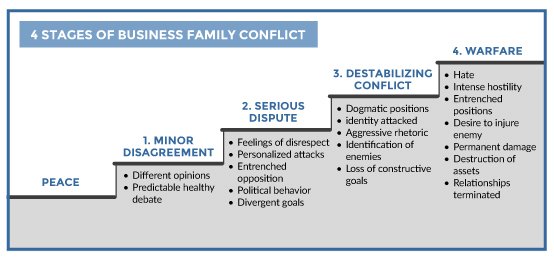
Interpersonal conflicts can be categorized into four types. Kickoff, at the everyman grade of friction, there are minor disagreements. These ascend from seeing things differently, and are usually worked through with respect and compromise. Some companies even engineer this kind of debate in order to drive fresh thinking–a tactic that Harvard Concern School professor and innovation expert, Linda Colina, calls "creative abrasion."ane When disharmonize of this nature is well managed, differing opinions lead to better solutions than those that would ascend from a singular signal of view. Merely yous want to baby-sit against creative chafe morphing into personalized attacks and entrenched opposition, where parties are and then poised to find things to disagree about.
Escalate, prolong and peculiarly personalize the level of discord, and yous enter the realm ofserious disputes. These may exist the consequence of larger ideological differences or may beginning as minor disagreements that fester and grow, especially in the confront of divergent goals. Feelings of disrespect combined with blame and defensiveness oftentimes come into play. These conflicts are nonetheless able to be worked through but must exist addressed quickly and competently. You especially desire to interrupt the alien parties from recruiting allies to their cause, or you lot take a chance moving to the side by side stage.
Then, at that place aredestabilizing conflicts, where factions develop, stakes and rhetoric escalate, and participants find it more and more than difficult to dorsum away from their positions in order to find an acquiescent resolution. These conflicts are dominated by dogmatic positions and emotions; anxiety is high, anger is expressed aggressively, and parties oftentimes feel their identity attacked. Without outside intervention, these conflicts are likely to develop into the most unsafe type of conflict: warfare.
Warfare can threaten the being of an organization or relationship. At this stage, positions are so entrenched that for some people it becomes more of a priority to exist right, or even to injure the other party than to discover a resolution to the disharmonize. Intense hostility may cause participants to attack i another personally and enact revenge at the expense of the family or business. Relationships that endure this stage of conflict are oftentimes permanently damaged, and families and companies tin be inexorably changed, divided, or even destroyed. The decades-long battle between the Demoulas cousins over their $4 billion supermarket chain, Market Basket, culminated in 2014 with the most expensive lawsuit in Massachusetts history. The cousins parted ways, with buyouts and restructuring of the buying group, allowing one co-operative to save what was left of the visitor. Often the only resolution to warfare is the separation of financial avails; family unit relationships rarely recover.
Disharmonize in a business family can happen over legitimate and of import differences, and also over real injury, merely it can likewise happen, or be accelerated, because of emotional insecurity; overreaction to perceived slights; misinformation and gossip; and manipulation past those who hope to gain from the discord. In a business organization family, the bug don't have to be big to get a family enflamed. Sometimes, seemingly minor bug (to an outsider) tin can offend sensibilities, create mistrust, and launch a family on a path to escalating conflict.
Family Dynamics and the Family Business concern
Business families have certain qualities that make them likely breeding grounds for intense feelings and human relationship conflicts.
Complex, Close Relationships
First—similar all families—in business families, the relationships between parents and children, among siblings and cousins, and fifty-fifty between more than afar relatives are often complicated. They come with strong attachments, high levels of dependency, and emotional reactivity. Families are complex systems: they are emotional past nature, with impassioned feelings, long histories, and indelible memories. Roles that are established early on in life are rarely updated, even as individuals mature and see themselves differently; family members can be too shut to encounter one another as conspicuously every bit outsiders exercise.
The emotional closeness of family members can be a source of both profound back up and greater tension. Family members tin can be protective, loyal and self-sacrificing. The inherent and heightened need in these systems for attending and blessing tin lead to competition amongst members. Expectations, assumptions, and favoritism–whether real or imagined–have greater influence in a family unit, where individuals are sensitive to the perception of "fair" treatment. Because the reputation of the family is determined past the actions of family members, individuals can feel steered, judged, or pressured to meet the expectations of the family over their own private needs. Given the many intrinsic tensions in families, it is not surprising that families that constructively piece of work together to counter these complexities stay together longer.
Entrenched Communication Patterns
2d is the unique communication style of the family unit of measurement. People tend to exist less careful in choosing their words with those closest to them. That kind of candid expression, which is oft beneficial to getting things done, tin can easily slip into callousness and lack of sympathy. Even certain words, expressions, or body language tin can be fraught with pregnant among people who know each other intimately, and their unconscious use tin can atomic number 82 to outsized reactions. Family members too have difficulty listening to ane another without judging, which tin can lead to caution and anticipation most existence open up with one another. That can further undermine mutual agreement exactly when it is nigh needed. Add to that the unfortunate, universal truth that family members are generally unskilled at expressing appreciation to one another. These communication patterns get entrenched in families over years of repeated apply.
Attachment to Legacy
Tertiary, in a business organisation family, there is by and large a heightened attachment to the legacy of the family. Nigh family owners consider themselves a permanent ownership grouping that is effectively closed; walking away from the family is rarely considered an option. Business concern family members can also be dependent on the business organization or the family for fiscal support, social status, or other reasons. They can also experience very sentimentally tied to the business that their ancestor founded and passed downwardly, and which becomes an of import part of the family members' personal identities. Given the high level of interdependence in these families, compromising on issues and working to achieve common goals seems logical. Under these weather, notwithstanding, it is piece of cake for family members to experience competitive, self-protective, controlling, and vulnerable. Business family members mostly take a sense that the stakes in their relationships are high, but also that their status in the system needs to exist protected.
Multiple Overlapping Roles
Finally, business family members have diverse roles–such equally family unit member, owner of the company, employee in the family business, board fellow member–that define their identify in the family business arrangement, and often their power and status in the system. When these roles overlap, a family member can feel role confusion. A parent can interact with a next generation member not only as a parent but also every bit a boss and business partner, which can arrive challenging to know how to care for one's relative in whatever circumstance. With overlapping roles, competing interests also more naturally arise, increasing the chances for misunderstanding or conflict.
The overlapping spheres of family, business, and ownership are important because the conflict in one expanse tin seep into the others easily and quickly. A family conflict can impede business concern relations and decisions; a difference at work tin can make interacting in the family more hard. Business families demand to manage bug in all iii spheres and be disciplined to non let conflict in one area infect another surface area of the family's life.
Conflict: A Case Study
Left unchecked, a disharmonize will escalate through a predictable path.
Permit'southward use the example of two siblings, Jane and Tim, who were fifty/50 partners in their retail business organisation. They began with aminor disagreement about the best way to remain competitive in the market. If they had opted for an open dialog at this bespeak, with objective input from the lath, they most likely could accept found a mutually adequate solution. Unfortunately, when they disagreed, Tim felt that Jane's objections were a sign of disrespect: that she believed that he was an ineffective manager.
Instead of being resolved, information technology escalated to aserious dispute. Rather than being near tangible business concern issues, with a shared goal of finding a resolution, the dispute became more and more about personal feelings and accusations. Jane and Tim demonstrated their power by excluding 1 another from important conversations and surprising one some other with decisions. They began calling each other names in private. This went on for several years, during which fourth dimension, the two branches of the family unit grew apart. Management wasted fourth dimension navigating the disharmonize; productivity and morale slowed.
At this indicate, Jane sought outside assist to try to mend the human relationship and the business, which was suffering. But the situation had go adestabilizing disharmonize. Tim saw Jane'due south attempt at a resolution as a sign of weakness and decided to printing for "victory." He took various steps to gain greater control of the company by hiring his sons-in-law and giving them wider responsibilities, without making Jane aware. Jane retaliated past encouraging some senior managers to arrive difficult for Tim's sons-in-law to succeed in the visitor. When conversations took place between them, they were heated. The siblings' spouses and children did non socialize.
For the first fourth dimension, both siblings began to consider options that would remove the other branch from the organization completely. Just when Jane presented options for how to dissever successfully (splitting operations, a buyout, etc.), Tim refused to hold to any idea. He finally admitted that he was in a stage ofwarfare now, where his principal goal was to hurt Jane and her family in whatever way he could.
And, in a mode, he did. While this boxing had been raging within the family unit, summit talent in the company had departed; competitors had taken advantage of their slow decision-making and made serious inroads. Both siblings blamed the other for the company'south failing marketplace share. Within a few years, the company was bankrupt and the family was bought out at a ridiculously low price. Similar the untended pleached tree, the diverging branches had weakened the entire system.
Of course, no family wants to see this kind of damaging escalation of conflict. And they don't have to. There are effective approaches to disagreement and negotiation techniques that can assistance all parties feel understood and role of the process, with positive results for family unity and business concern success.
ane Linda A. Hill, Greg Brandeau, Emily Truelove, Kent Lineback, Commonage Genius: The Art and Practise of Leading Innovation (Boston: Harvard Business concern Review Printing, 2014).
Professor John A. Davis

Founder and Chairman, Cambridge Family Enterprise Grouping; Senior Lecturer and Faculty Manager, Family Enterprise Programs, MIT Sloan School of Management
John A. Davis is a globally recognized pioneer and authority on family enterprise, family wealth, and the family function. He is a researcher, educator, writer, builder of the field's most impactful conceptual frameworks, and advisor to leading families effectually the world. He leads the family enterprise programs at MIT Sloan. To follow his writing and speaking, visit johndavis.com and twitter @ProfJohnDavis.
Courtney Collette

Partner and Senior Counselor, Cambridge Advisors to Family Enterprise; COO, Cambridge Institute for Family unit Enterprise
Courtney Collette is Main Operating Officer of the Cambridge Institute for Family unit Enterprise, a research and education institute devoted to multigenerational family unit enterprises. Since 2011, she has led its teaching programming, conferences, inquiry studies, and publications. Every bit head of education programming, Ms. Collette designs curricula for seminars, workshops, and online courses for family unit enterprise audiences worldwide including bespoke private programs for individual families and organizations. She has authored several publications pertaining to the success of family unit enterprises, including articles, Harvard instance studies, and the book, Next Generation Success, a 10-year study of side by side generation talent development in global family unit enterprises. Ms. Collette spent a decade as a trusted advisor to concern families on the issues of governance, family relationships, succession, and side by side generation readiness.
loureirograsintud.blogspot.com
Source: https://cfeg.com/insights_research/understanding-conflict-in-the-family-business/
0 Response to "How Much Conflict Is Acceptable in a Family"
Post a Comment